How To Install Ati Drivers Ubuntu Terminal

How Hardware Drivers Work on Windows. When you install Windows, you’ll need to install hardware drivers provided by the hardware’s manufacturer — motherboard chipset drivers, graphics card drivers, Wi-Fi drivers, and more.
• • • • • With Ubuntu 14.04 and other Linux distributions, you have the choice to use open- or closed-source drivers for hardware that benefits from proprietary software. Ubuntu automatically updates installed drivers and notifies you of proprietary upgrades, but you still need to know a little about your hardware to choose the best drivers. The Linux kernel includes open-source modules -- i.e.
Drivers -- for most hardware, and Ubuntu loads these modules from a boot archive called initramfs. You can blacklist unwanted modules or load specific modules by updating initramfs.
Credit: diawka/iStock/Getty Images Improved Functionality With Proprietary Drivers Step Press the 'Super' key -- also called the Windows key -- then type 'Additional Drivers' (without quotes) and press 'Enter.' If any proprietary drivers are available for your system, Ubuntu finds them and recommends the best ones for your hardware. Step Select a driver from the list. If proprietary drivers are available for several components, such as wireless cards, video cards or sound cards, you can install drivers for each device. Download video membaca huruf hijaiyah. Updating Installed Modules Step Open Gnome Terminal to update your system using APT package manager. Enter the following command to synchronize your package list and install all available updates: sudo apt-get update && sudo apt-get dist-upgrade The command 'dist-upgrade' ensures that APT resolves all package dependencies during the upgrade. Step Enter 'lsmod' at the prompt to print a list of loaded modules.
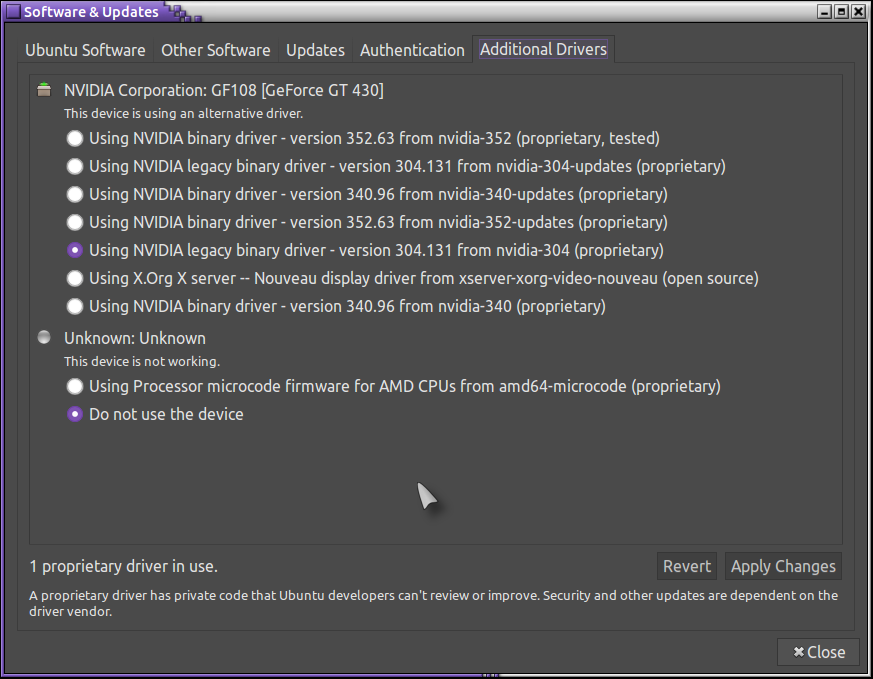
If you're updating drivers because some of them don't work, you must try blacklisting the ones included with Ubuntu and loading others until your hardware starts working. This process is usually only necessary for older hardware since Ubuntu is designed to work as seamlessly as possible with newer hardware. Gksudo gedit /etc/modprobe.d/blacklist.conf Add any modules you want to blacklist to the end of the file. For example, blacklist the open-source wl wireless module by adding the following line to the file: blacklist wl To find out which modules you need to blacklist, you must search the Ubuntu website for the hardware component you're trying to get working (link in Resources). Step Open the file /etc/modules in Gedit to add the names of modules you want to load at startup. Place one module name per line as in the following example.
AMD drivers can be a little trickier depending on whether you want to use proprietary drivers or not. By default, Ubuntu uses the open-source Radeon drivers when it detects an AMD graphics card in the system. These drivers are maintained by a team employed by AMD and are more up to speed than the Nvidia open-source drivers. In many games, you may not even notice a difference between the two. However, the closed-source Catalyst driver (also known as the fglrx driver) is made available for those who would like to use it.